Why Everyone’s Talking About NMN | Supplements in 2025?
September 05
Aging is an inevitable part of life, but recent scientific breakthroughs suggest it may be possible to slow the process. Among the most promising discoveries is nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), a naturally occurring compound now at the center of anti-aging research.
NMN is a nucleotide—the building block of DNA—present in all living cells. In humans, it plays a key role in essential biological functions, from energy production and brain health to skin vitality, weight management, and even sleep quality. Its importance stems from being the direct precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺), a vital coenzyme that fuels metabolism, supports DNA repair, and maintains cellular health.
Over the past few years, NMN has gained significant attention for its potential to counteract age-related decline. Studies suggest that by boosting NAD⁺ levels, NMN supplementation may not only promote healthier aging but also provide therapeutic value for metabolic disorders and other age-related conditions.
As global populations continue to age, interest in NMN’s therapeutic potential grows stronger. In this blog post, we’ll explore what NMN is, how it works, and the wide range of potential benefits it offers for both longevity and overall well-being.

What Exactly Is NMN?
NMN is not merely a dietary supplement; it’s a crucial component of cellular health1, acting as a precursor to NAD+, a molecule vital for energy metabolism and cellular functions.
Found naturally in the body, NMN’s role is to support the production of NAD+, thereby influencing various processes, including DNA repair, metabolic activities, and energy production. Its presence is akin to providing the raw materials necessary for the intricate machinery of our cells to function optimally.
Within our cells, NMN contributes to the synthesis of NAD+, directly affecting our cellular energy and the maintenance of healthy physiological functions.
As we age, NMN levels decrease, leading to reduced NAD+ production and the onset of age-related decline. Supplementation with NMN2 can potentially replenish NAD+ levels, supporting cellular health and longevity.
The Promised Benefits and What Science Actually Says
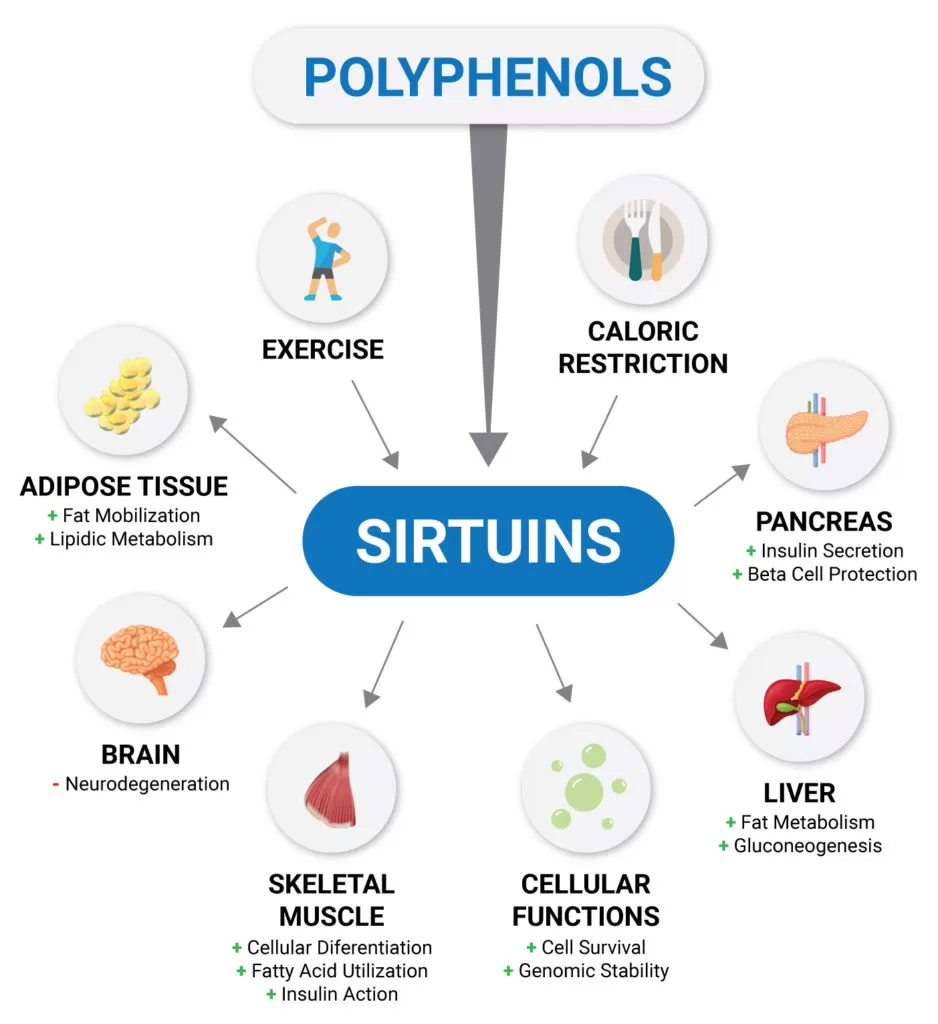
Activating sirtuins to slow the aging process
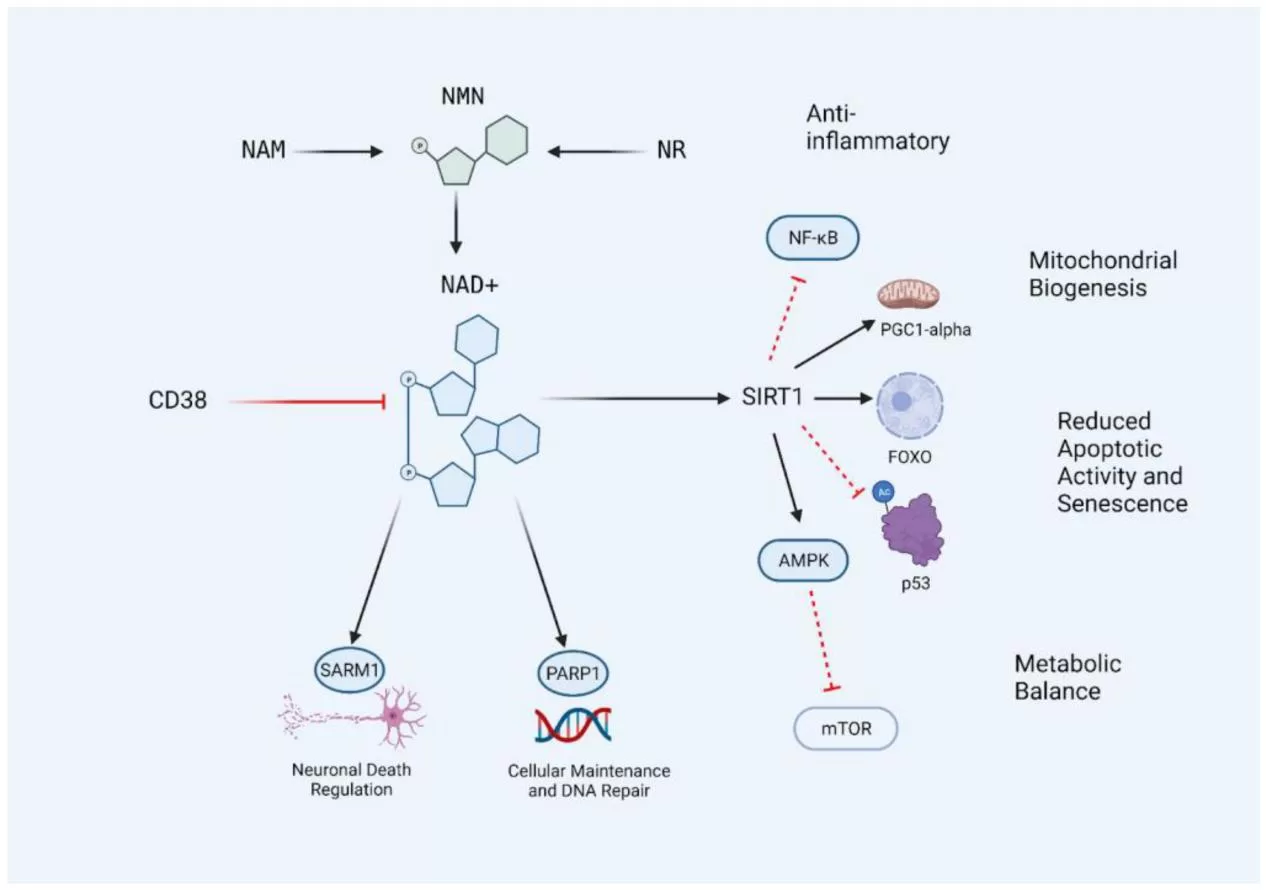
The human body utilizes a variety of small molecules called coenzymes to facilitate chemical reactions. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is one such coenzyme, composed of nicotinamide and adenine nucleotides linked by a phosphate bond.
NAD+ is involved in numerous metabolic processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation.
As we age, our NAD+ levels decline, which is associated with decreased energy production, increased DNA damage, and impaired gene expression. This decline in NAD+ levels may contribute to age-related declines in cellular function and the development of age-related diseases.
Recent studies have shown that NMN can help slow the aging process in animals. It is not yet clear whether NMN has the same effects in humans, but the evidence so far is encouraging.
NMN has also been shown to significantly affect the activity of sirtuins, a class of enzymes that play a role in aging and age-related diseases. Sirtuins are involved in a variety of functions, including DNA repair, cell division, and cell death.
The discovery that NMN is a potent regulator of sirtuins may have important therapeutic implications for a variety of diseases.
Boost exercise energy levels
NMN has been shown to boost energy levels and stamina. A randomised control trial published in 2021 tested NMN in 48 middle aged amateur runners in training for six weeks. The group taking NMN had a significantly increased aerobic capacity and better endurance than the control group .
NMN is thought to work by increasing the production of mitochondria, the powerhouses of cells. This, in turn, leads to increased energy production and improved stamina. NMN has also been shown to protect cells from damage during training due to the increased oxygen capacity of skeletal muscle.
Improve cognitive function
Several animal studies have shown that NMN can improve cognitive function. NMN is thought to work by helping to protect and repair nerve cells, which can decline with age. This can lead to improved memory, focus, and other cognitive functions.
A large review study published in August 2022 concluded that NMN could be effective for different forms of dementia including age-related decline.
While NMN shows promise as a cognitive enhancer, more research and head-to-head studies are needed to confirm its efficacy in humans. It is, however, already being used by practitioners as a treatment for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease to support brain health.
Improve skin health and delay skin aging
The benefits of NMN for skin health are well-documented and include improved complexion and fewer signs of ageing.
Recent studies have shown that NMN supplementation can improve the appearance of the skin by reducing inflammation and stimulating collagen production. NMN has also been shown to protect the skin from damage caused by UV exposure.
The activation by NMN of certain proteins, called sirtuins, protects against multiple skin ageing related issues including wound healing, wrinkles, UV, and skin cancers .

Enhance immunity
NMN is a compound that has been shown to boost immunity. In a recent study, NMN was found to increase the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infection. NMN is thought to work by stimulating the production of a protein called Interleukin-6, which is involved in the immune response.
This is good news for people who are looking for ways to boost their immune system and reduce inflammation because NMN is a safe and natural compound that is available over the counter.
Weight loss
There is growing evidence that NMN can help with weight loss by activating the sirtuin gene. Sirtuin is responsible for regulating metabolism, and by activating it, NMN can help to boost metabolism and burn more fat.
In one study, mice that were given NMN lost weight and had lower levels of body fat than those that were not given NMN. Additionally, they also had higher levels of energy and stamina.
Although NMN is not a weight loss supplement, when combined with calorie restriction it will improve insulin sensitivity and will improve metabolic flexibility, which in turn leads to increased weight loss.
What to Expect If You Try NMN?

5 HOURS: NAD+ levels begin to rise
Studies in humans show increased levels of NAD+ metabolites in blood plasma within the first few hours of NMN supplementation—and they continue to rise steadily, suggesting increased utilization of NAD+ in cells and tissues. Cells are already taking advantage of increased NAD+ levels to support hundreds of critical cellular processes.
3 DAYS: NMN promotes mitochondrial health and cellular energy production
NAD+ levels continue to rise, now benefiting the cell’s powerhouses and the place where cellular energy is made: the mitochondria. A preclinical study demonstrated that treatment of human kidney cells in culture with NMN for three days resulted in increased mitochondrial replication.
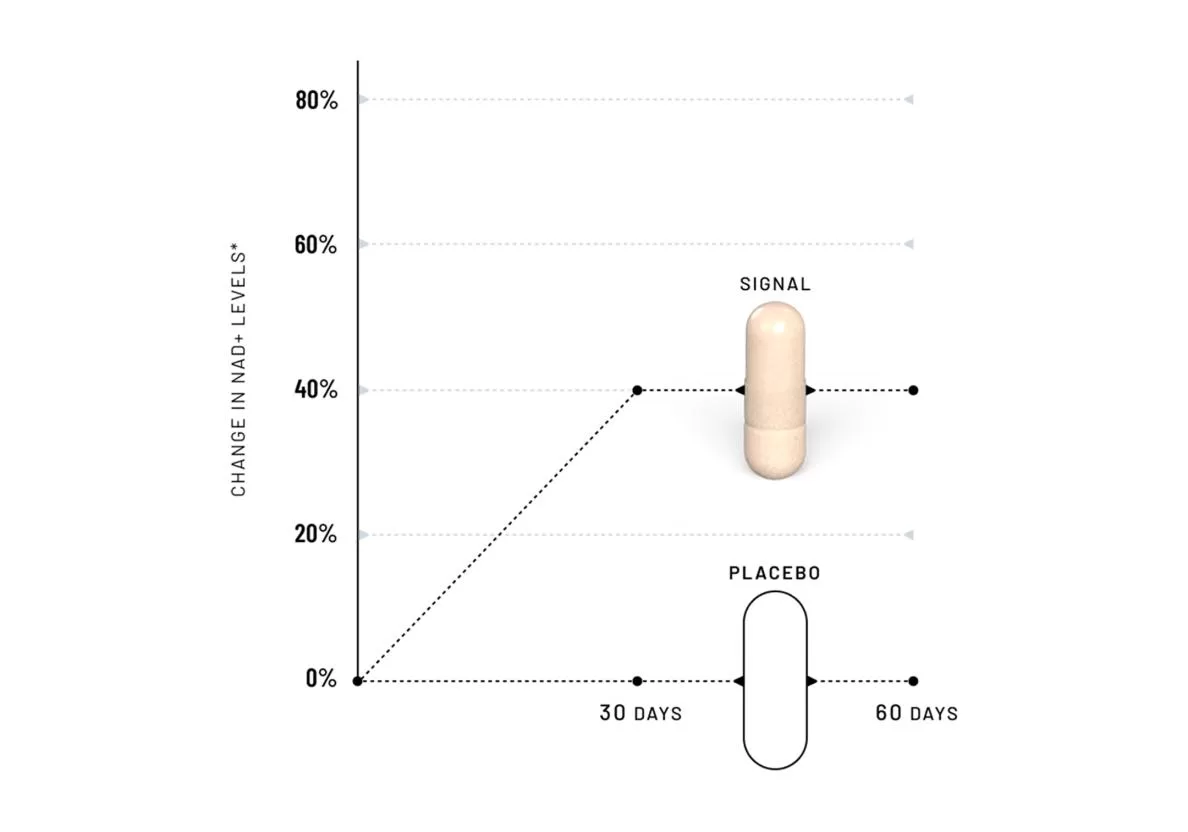
1 MONTHS: NMN increases NAD+ levels by 40%
A human clinical study examining NMN supplementation at a dose of 250 mg per day in healthy adults showed 40% higher NAD+ levels in the blood compared to placebo at 30 days. This is the same dose found in Signal.
6 WEEKS: NMN and muscle benefits
A human clinical study found that oral supplementation of NMN at a dose of 250 mg per day for 6 weeks partly improved muscle strength and performance in healthy older men.
Another human clinical study published in Nature Aging demonstrated that NAD+ was one of the most depleted metabolites in aging muscle and that high levels of NAD+ were associated with healthy muscle function.
8 WEEKS: NMN and skin benefits
Advanced glycation end products, or AGEs, are markers of skin aging. A small clinical trial involving healthy postmenopausal women found that NMN supplementation for eight weeks at 300 mg of NMN per day resulted in decreased AGEs in the skin.
3 MONTHS: NMN supports gait speed
It’s been three months, and you’ve logged 60 days of 40% higher NAD+ in your cells and tissues. Benefits at the cellular and tissue level are beginning to translate to functional benefits. One clinical trial found an improvement in gait speed (translation: walking speed) in healthy, elderly men who took 250 mg of NMN per day.

6 MONTHS AND BEYOND: Healthy aging and NAD+ go hand-in-hand
With consistent use, the sustained, elevated levels of NAD+ at six months and beyond are supporting your overall well-being and health. NAD+ declines by as much as 50% every 20 years, according to research.
It’s important to maintain your NMN supplementation: Research shows that four weeks after discontinuation of NMN, NAD+ levels returned to pre-supplementation levels. Just like with exercise, sleep, and diet—consistency is key for long-term results. Human studies are beginning to show that healthy aging and NAD+ abundance go hand-in-hand.
Is NMN Safe? Risks and Controversies
NMN is an excellent supplement for boosting cellular NAD levels, as it’s well-tolerated and has shown minimal side effects in both human and animal studies.Research in humans indicates that daily doses of up to 1,200 mg are safe.
Before adding any supplement to your routine, be sure to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss your individual needs as well as the potential risks and benefits.
What Are the Long-Term Risks of Daily NMN Use?
- Risks include biological, economic, and regulatory issues.
- Carcinogenicity: NAD⁺ may help survive precancerous lesions or malignant tumors.
- Adverse effects: Up to approximately 20% of users report mild symptoms.
- Regulatory ambiguity: FDA exclusions, processing of NDI applications, and pending litigation create market instability.
- Product inconsistency: Studies have found discrepancies of up to 28% between the labeled and actual NMN content in supplements.
- Cost: Monthly costs typically exceed $50–150, with no proven long-term benefits.
What are the dangers of NMN?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is generally safe for most people when taken at recommended doses. However, some users may experience mild side effects such as nausea, stomach upset, diarrhea, headache, fatigue, or insomnia.
These symptoms are generally temporary and resolve after discontinuing the medication. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting NMN supplements, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
What is the controversy with NMN?
The primary controversy surrounding NMN revolves around its regulatory status and the robustness of supporting scientific evidence. In 2022, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) excluded NMN from the definition of a dietary supplement, citing its investigation as a drug.
This decision led to legal challenges from industry groups. While enforcement of this ruling was paused in 2024, the debate continues regarding NMN’s classification and the need for further clinical trials to confirm its efficacy and safety.
NMN vs. Other Longevity Supplements
Research suggests that both NR and NMN are effective in raising NAD levels, but there are some differences between the two.
Studies have shown that our bodies convert NR into NMN through a series of metabolic processes before being further metabolized into NAD. This means that NR requires an additional step before it is actually converted to NAD for the benefits.
Meanwhile, NMN is directly converted into NAD without the need for further intermediates, making it a better and more efficient choice for rapidly increasing NAD levels compared to NR.
Can NAD Supplementation Increase NAD Levels?
Recent research suggests that supplementing with NMN may be more effective than taking NAD directly. This is because NAD, with its large and complex molecular structure, is poorly absorbed through the digestive system and not easily taken up by cells—making it impractical for oral use.
In contrast, NMN is a smaller molecule and a direct precursor to NAD. It can enter cells through a specific receptor and is then converted into NAD by enzymes inside the cell. Human studies have shown that oral NMN supplementation can significantly increase NAD+ levels in the body.
Therefore, if your goal is to boost NAD levels, NMN supplementation may offer a more practical and effective solution than NAD itself.
Food Sources of NMN: Can You Eat Your Way to Longevity?
NMN is present in various foods, though typically in small amounts.
Here are some of the top natural sources:
- Edamame: Approximately 0.47-1.88 mg per 100g serving.
- Broccoli: Around 0.25-1.12 mg per 100g serving.
- Avocado: Estimated 0.36–1.60 mg per 100g serving.
- Cabbage: Roughly 0.90 mg per 100g serving.
- Cucumber: About 0.60 mg per 100g serving.

Comparing NMN Content in Food vs. Supplements
While it is clear that NMN is present in a variety of foods, the amounts are relatively small. For example, to obtain just 1 mg of NMN, you would need to consume nearly 150g of broccoli or more than 110g of cabbage. Achieving a daily intake of 400 mg of NMN would require consuming impractically large quantities of these foods.
In contrast, NMN supplements offer a convenient way to achieve optimal NAD+ levels without the need to consume massive amounts of food. A single NMN PerformMax supplement capsule contains 400 mg of NMN, making it much easier to maintain consistent NAD+ levels and support energy production and cellular health.
Should You Try NMN?
NMN shows promising anti-aging and health benefits in animal studies, and early human research suggests it’s safe and may support energy, focus, and metabolism. However, evidence in humans is still limited, and side effects like digestive issues are possible.
Before starting NMN—or any supplement—consult your doctor to weigh potential risks and benefits. For best results, pair NMN with a healthy lifestyle that includes quality sleep, regular exercise, and balanced nutrition.
Conclusion
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is seen as a major step forward in anti-aging research, and ongoing human clinical trials are expected to confirm its potential to improve health and vitality by boosting NAD+ levels.
While animal studies have shown promising results in areas such as metabolism and physical activity, future research will focus on determining NMN’s safety and efficacy in humans. Larger human trials are underway, and more data are expected to be released soon.
Get in Touch
If you have any questions, please contact our experts, we are always ready to help you with individual formulations, private label solutions or any other requirements to kick-start your brand!
