A balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle are well-known foundations of long life and vitality. But modern research is uncovering additional factors that can further support healthy aging. Among them, one compound stands out — spermidine.
Spermidine is a naturally occurring polyamine found in all living organisms. Studies have linked it to a range of anti-aging benefits, including improved heart health, enhanced cognitive function, and even longer lifespan. It plays a key role in autophagy—the body’s natural process of removing damaged cells and regenerating new ones—helping to maintain optimal cellular function as we age.
In this article, we’ll explore what spermidine is, how it works, where it’s found, and what science says about its potential to promote longevity and overall well-being.

What Is Spermidine?
Spermidine is a naturally occurring polyamine compound first identified in 1678 by the scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, who discovered it in semen—hence its name. Found in all living cells, spermidine plays a vital role in cellular growth, repair, and renewal, as well as in stabilizing DNA, RNA, and proteins. It supports many key metabolic processes, helping maintain the body’s overall cellular balance.
This compound is abundant in certain foods, including wheat germ, soybeans, aged cheese, mushrooms, and various fruits and vegetables. It also occurs naturally in the human body, where it facilitates autophagy—the process by which cells recycle damaged components to stay healthy and function efficiently.
As we age, our natural spermidine levels decline, contributing to cellular aging and increased risk of age-related diseases. Fortunately, you can help replenish spermidine through a nutrient-rich diet, supplementation, and by supporting a healthy gut microbiome, which also produces spermidine naturally. Maintaining optimal levels may promote longevity, cellular vitality, and overall well-being.
How does spermidine work?
Spermidine has been found to play a significant role in promoting longevity. Its potential to extend healthspan is thought to be due to several factors:
Inducing Autophagy
Autophagy is a vital cellular process responsible for the degradation and recycling of damaged or unnecessary cellular components. Acting as the cell’s internal cleaning system, it removes misfolded proteins and dysfunctional organelles, thereby maintaining cellular health and preventing the buildup of elements that can contribute to disease and ageing.
Among known autophagy inducers, spermidine stands out as a potent natural compound. It activates specific cellular pathways that promote the clearance and renewal of cellular components—a mechanism strongly associated with anti-ageing benefits.
Research supports these effects:
A study published in Nature Cell Biology demonstrated that spermidine supplementation extended the lifespan of yeast, flies, worms, and even human immune cells.
Another study in Science found that spermidine protects against age-related oxidative stress in mice, further highlighting its potential to promote longevity.
As scientific understanding of autophagy deepens, its role in health and longevity becomes increasingly evident. By sustaining efficient cellular maintenance and renewal, autophagy may help slow the ageing process and lower the risk of age-related diseases, offering a promising avenue for healthy ageing.
Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense against injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can damage tissues and accelerate ageing.
Spermidine helps counter this by inhibiting key pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, reducing excessive immune activation and promoting balance.
Studies have shown that spermidine suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress in immune cells and animal models, supporting its potential to combat chronic, age-related inflammation and maintain cellular health.
Protecting DNA from Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when the production of free radicals exceeds the body’s ability to neutralize them. These unstable molecules can damage vital cellular components—especially DNA—accelerating ageing and increasing the risk of age-related diseases.
Spermidine helps safeguard DNA by enhancing the expression of genes involved in DNA repair, supporting the production of protective proteins that prevent harmful mutations. Additionally, spermidine can directly scavenge free radicals, neutralizing them before they inflict cellular damage.
By reducing oxidative stress and preserving DNA integrity, spermidine promotes cellular resilience, supports healthy ageing, and may contribute to longevity.
Modifying the Immune Response
The immune system is the body’s defence network against pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. However, as we age, immune regulation often declines, increasing vulnerability to infections, chronic inflammation, and autoimmune disorders.
Spermidine helps modulate immune activity by enhancing immune cell function and promoting a balanced response. This balance is key to preventing excessive inflammation and maintaining immune resilience.
Research supports these effects:
A study in Nature reported that spermidine improved immune function and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans, a model organism for ageing research.
Another 2019 study found that reduced insulin signaling—a pathway linked to lifespan extension—alters spermidine metabolism, suggesting that higher spermidine levels may contribute to immune optimization and healthy ageing.
By fine-tuning immune responses and supporting cellular balance, spermidine may play a vital role in maintaining immune health throughout ageing.
Why is wheat germ the Richest Natural Source?
Wheat germ is a rich natural source because it is a highly concentrated package of nutrients, including high levels of vitamin E, B vitamins, essential amino acids, healthy fats, and minerals like magnesium, zinc, and phosphorus. It contains significantly more vitamins, minerals, and fats than standard wheat flour and is especially notable for being the richest plant source of alpha-tocopherol (a form of vitamin E) and a key source of polyamines like spermidine.
Nutrient-dense composition
- Vitamins: Wheat germ is particularly rich in vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) and B vitamins, such as folate, thiamin, and B6.
- Minerals: It is a powerhouse of minerals, including magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, and potassium.
- Protein: It provides high-quality plant-based protein with a good profile of essential amino acids, comparable to proteins found in eggs and milk.
- Healthy fats: Wheat germ is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids.
- Phytochemicals: It contains beneficial compounds like phytosterols and antioxidants.
- Dietary fiber: It is an excellent source of dietary fiber, which aids digestion and helps regulate cholesterol.
Wheat germ is an excellent dietary source of spermidine
Research data shows that wheat germ contains spermidine at levels as high as 0.8-2.4 mg/g, significantly higher than other common plant foods. For example, compared to common grains, vegetables, and fruits, the spermidine content in wheat germ can be several or even dozens of times higher. This makes wheat germ an ideal raw material for spermidine extraction.
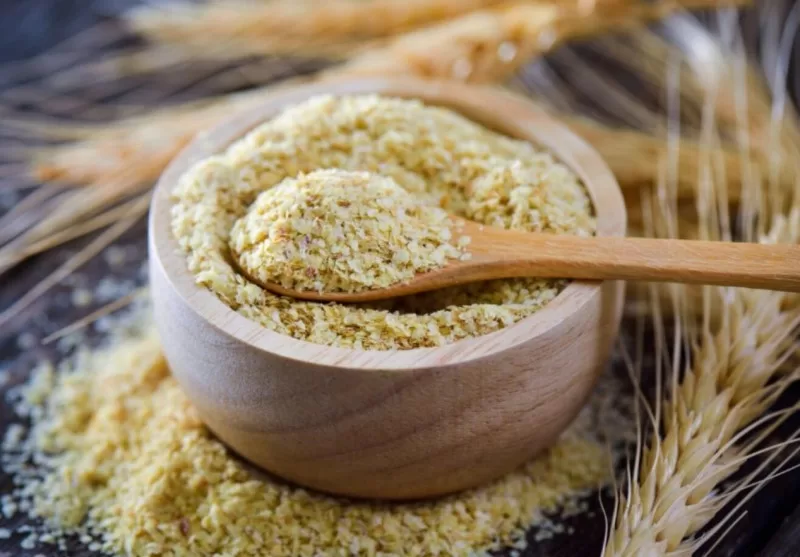

- Industrially isolated wheat germ contains 220-337 μg/g of total polyamines, with spermidine being one of the most abundant polyamines.
- Wheat germ fractions contain higher concentrations of bioactive compounds compared to refined grain products.
- Wheat germ has been specifically identified as one of the major natural sources of spermidine, along with aged cheese, nuts, soy, and various fermented products.
Health Benefits of Spermidine from Wheat Germ
Cellular Rejuvenation and Anti-Ageing
One of the most promising spermidine benefits involves cellular rejuvenation. Spermidine helps trigger autophagy, the body’s process of recycling worn-out or damaged cell components. This cleanup supports healthier, longer-living cells.
In studies, spermidine has been shown to:
- Support DNA repair and protein balance inside cells.
- Reduce the buildup of cellular waste that contributes to ageing.
- Help maintain energy production and cellular efficiency.
By keeping this renewal cycle active, spermidine may help preserve the body’s ability to repair itself and maintain youthful function over time.

Longevity Support
Spermidine is often linked with healthy lifespan extension, mainly based on animal research. In studies with yeast, flies, and mice, spermidine supplementation appeared to lengthen lifespan and improve cellular resilience.
Observational studies in humans have also noted that people who consume spermidine-rich diets tend to have lower mortality rates, especially from heart disease and certain cancers.
While these findings don’t prove cause and effect, they hint at a strong connection between spermidine intake and long-term health.
Researchers believe spermidine works by activating similar biological pathways to those triggered by calorie restriction, one of the most studied longevity strategies.
Cardiovascular Health
Spermidine’s potential to support heart health has gained attention in recent years. In animal studies, regular intake appeared to:
- Improve heart muscle flexibility and performance.
- Support healthy blood pressure by relaxing blood vessel walls.
- Reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in heart tissue.
Long-term research in mice also showed that those given spermidine lived longer and maintained stronger cardiac function. Human studies echo this trend, linking higher dietary spermidine to better cardiovascular outcomes.
These effects are believed to stem from spermidine’s influence on autophagy and its gentle anti-inflammatory properties, both of which help the cardiovascular system function more smoothly with age.
Lipid Metabolism and Weight Regulation
Spermidine also seems to influence how the body handles fats and energy. Research in animals suggests it may improve lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity, both of which are vital for metabolic balance.
Findings include:
- Better fat breakdown in high-fat diet conditions.
- Improved blood sugar control through enhanced insulin response.
- Increased thermogenesis, or natural fat burning, at the cellular level.
These results point toward a possible role for spermidine in supporting healthy weight management and metabolic function, though human data remains limited.

Neuroprotection and Cognitive Health
Spermidine is being studied for its role in brain protection and cognitive function. In aging models, spermidine supplementation has been observed to support memory and protect neurons from damage.
It appears to work by promoting autophagy in brain cells, which helps clear toxic proteins linked to cognitive decline. Spermidine also supports mitochondrial energy production, which keeps brain cells active and healthy.
In one human trial involving older adults, spermidine supplementation showed no significant improvement in memory compared to placebo, though researchers noted the dose used might have been too low to see full effects.
Overall, findings suggest spermidine may help maintain brain health as part of a long-term lifestyle approach.
Potential Cancer Prevention
Early evidence hints that spermidine could support the body’s natural defenses against certain cancers. In lab studies, it has been shown to help regulate cell growth and promote autophagy, which removes damaged or precancerous cells before they multiply.
Researchers have observed particularly strong effects in liver and colon tissues, where spermidine appears to slow abnormal cell activity and reduce tumor formation in animal models.
While this area of research is still in its early stages, spermidine’s role in maintaining normal cell turnover makes it a compelling topic for future cancer prevention studies.
Immune System Modulation
Spermidine plays a role in balancing the immune system. Research indicates it may encourage the formation of new immune cells while calming excessive inflammation that can damage tissues.
Studies suggest spermidine:
- Helps renew immune cells in aging bodies.
- Supports healthy gut bacteria that influence immune defence.
- May reduce inflammatory molecules associated with chronic disease.
This balancing effect helps the body respond to infections more effectively without triggering unnecessary inflammation, a key factor in healthy aging.
Spermidine vs. Other Longevity Compounds
Spermidine, Resveratrol, NMN, and CoQ10 have different primary functions: Spermidine triggers autophagy (cellular cleaning), Resveratrol is a potent antioxidant that activates longevity pathways, NMN boosts NAD+ for cellular energy and DNA repair, and CoQ10 generates cellular energy and has antioxidant properties. While all support healthy aging, they do so through distinct mechanisms.
Spermidine
- Mechanism: Stimulates autophagy, the body’s process for clearing out damaged cells and waste.
- Benefits: Promotes cellular renewal and health, which may support brain function and cardiovascular health.
- Sources: Found in foods like wheat germ, aged cheese, and mushrooms.
Resveratrol
- Mechanism: Activates longevity pathways (like SIRT1) and acts as a powerful antioxidant.
- Benefits: Combats oxidative stress and inflammation, supports DNA repair, and has potential benefits for skin, joint, and heart health.
- Sources: Found in the skin of red grapes, berries, and peanuts.
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Mechanism: A precursor to NAD+, which is essential for cellular energy production and DNA repair.
- Benefits: Increases NAD+ levels, supporting energy metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and cellular repair.
- Sources: Available as a dietary supplement.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
- Mechanism: Helps generate energy in the mitochondria and acts as an antioxidant.
- Benefits: Supports cellular energy production and helps protect cells from oxidative damage.
- Sources: Available as a supplement; the body also produces it naturally.
How to Add Spermidine to Your Routine?
Ensuring adequate spermidine intake can be beneficial for overall health, given its roles in cellular function, aging, and disease prevention. Here are some effective ways to incorporate spermidine into your daily life:
Dietary Sources
- Whole Grains: Foods like wheat germ, rice bran, and whole grain bread are rich in spermidine.
- Soy Products: Tofu, soybeans, and natto (fermented soybeans) are excellent sources.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and green peas contain significant amounts of spermidine.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Mushrooms, broccoli, cauliflower, and citrus fruits also contribute to spermidine intake.
- Cheese: Certain aged cheeses, such as cheddar and Parmesan, have high spermidine content.
- Nuts and Seeds: Sunflower seeds, hazelnuts, and almonds can provide a spermidine boost.

Supplements
For those who might find it challenging to obtain sufficient spermidine from dietary sources alone, spermidine supplements are available. These supplements are often derived from wheat germ extract and can help ensure consistent intake. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are another rich source of spermidine, thanks to the action of microorganisms that enhance polyamine content during fermentation:
- Natto: As mentioned, this fermented soybean product is particularly high in spermidine.
- Tempeh: Another fermented soybean product, common in Indonesian cuisine.
- Kimchi and Sauerkraut: Fermented vegetables like cabbage can contribute to spermidine intake.

Healthy Gut Microbiota
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential, as certain gut bacteria can produce spermidine. Probiotic-rich foods like yoghurt, kefir, and other fermented products can support gut health and, indirectly, spermidine levels.
Balanced Diet and Lifestyle
A balanced diet rich in various nutrients supports overall health and the body’s natural ability to synthesise and utilise spermidine. Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management are also important factors in maintaining optimal cellular function and metabolism, which includes spermidine metabolism.
Safety and Considerations
Spermidine is generally considered safe for most people, whether obtained from food or supplements. However, it may interact with certain medications—such as antidepressants or blood thinners. To ensure safety, it’s best to consult your healthcare provider before adding spermidine or any new supplement to your routine.
The Future of Spermidine Research
Future research on spermidine will aim to unravel its precise molecular mechanisms and identify therapeutic targets for age-related diseases. Key areas of focus include its role in autophagy induction, mitochondrial function enhancement, and its potential benefits in cognitive decline, cardiovascular health, and metabolic disorders.
Ongoing and upcoming studies will also seek to determine optimal dosages, evaluate synergistic effects with existing therapies, and explore spermidine’s potential as a dietary intervention to promote healthy ageing and longevity in humans.
Conclusion
Spermidine is far more than a trending term in longevity science—it’s a powerful, naturally occurring compound that supports cellular renewal and balance. By promoting autophagy, reducing inflammation, protecting DNA, and modulating the immune response, spermidine plays a central role in maintaining cellular health and resilience.
Its potential benefits span multiple systems—supporting cardiovascular and neurological health, blood sugar balance, bone strength, fertility, and fat metabolism—making it a promising ally in healthy ageing.
Incorporating spermidine-rich foods such as soybeans, mushrooms, and whole grains into your diet—or considering supplementation under professional guidance—can be a meaningful step toward a longer, healthier life. Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen.
