What Is Creatine Monohydrate?
Creatine is a compound found mainly in skeletal muscle, with small amounts also found in the brain. Creatine is produced by the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, but you can also get it through your diet from foods such as red meat and fish. Our bodies store creatine as phosphocreatine (primarily in the muscles) where it’s used as a source of energy.
Creatine monohydrate is a dietary supplement that consists of a creatine molecule and one water molecule, making it stable and easily absorbed by the body. It is the most studied form of creatine and helps improve muscle performance during short, high-intensity exercises by aiding in energy production and muscle recovery. While your body produces some creatine naturally and it is found in foods like meat and fish, supplements make it easier to reach higher levels.
Creatine monohydrate is a natural substance that can be converted into creatine phosphate in the body. Creatine phosphate helps make a substance called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP provides energy for muscle contraction; it is one of the most commonly used supplements that people use to build lean muscle mass, maximize performance, and increase strength.

What Foods rich in creatine?
1. Herring
Creatine: 1.25 grams per 4-ounce serving
Kippered herring is usually served with crackers or scrambled or poached eggs. Herring contains up to 5 grams of creatine per pound, or 1.25 grams per 4 ounces raw, which makes it one of the richest sources of creatine.
Just 100 grams (a little over 3 ounces) of kippered herring has nearly 25 grams of protein and contains 11% and 9.5% of the Daily Value (DV) for magnesium and potassium.
2. Beef
Creatine: 0.41 grams per 3-ounce serving
Lean cuts of beef contain 2 grams of creatine per pound (about 0.41 per 3-ounce serving). Lean beef is a high-quality protein offering essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and B vitamins, which support energy and overall health.
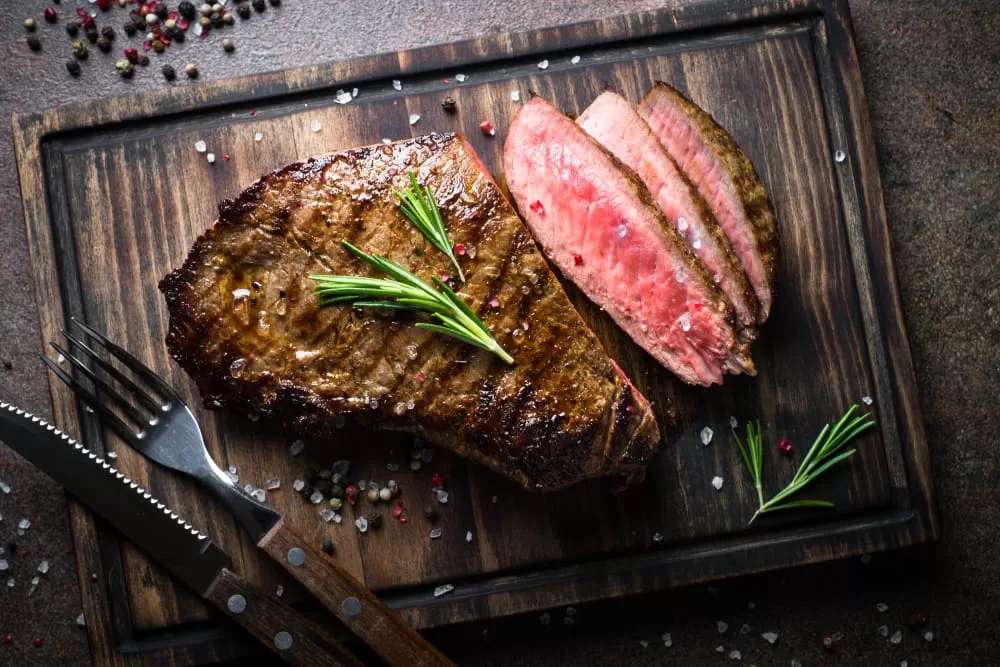

3. Salmon
Creatine: 0.5 grams per 4-ounce serving
Salmon contains up to 0.5 grams of creatine per 4-ounce serving (2.0 grams per 1 pound raw). Due to its higher fat content, salmon is a rich source of omega-3s, polyunsaturated fatty acids that support brain and heart health.
National Institutes of Health: Office of Dietary Supplements. Omega-3 fatty acids – health professional fact sheet.
Salmon is a source of protein. It also contains nutrients like calcium, potassium, and vitamins A and B12.

4. Chicken
Creatine: 0.41 grams per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving
Chicken is a relatively affordable and easily accessible high-quality protein. Skinless, boneless chicken contains 0.36–0.39 grams of creatine per 100 grams (about 3.5 ounces).The same serving also provides 22.5 grams of protein.
Choosing skinless chicken will reduce the saturated fat you eat.
5. Plaice
Creatine: 0.23 grams per 4-ounce serving
American plaice is a type of flounder. Plaice is in the same family as flounder, sole, and halibut. It is a flat fish with two right eyes found in the deep waters of the New England and mid-Atlantic regions.
Plaice contains 0.9 grams per pound (0.23 grams per 4-ounce serving).It is considered a lean fish because it has less than 4 grams of fat per 100 grams.
6. Cod
Creatine: 0.35 grams per 4-ounce serving
Cod contains 1.4 grams per pound of creatine, or 0.35 grams per 4-ounce serving. The same serving also delivers 20 grams of filling protein and nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D that strengthen your bones.

3. Tuna
Creatine: 0.45 grams per 4-ounce serving
Like salmon, bluefin tuna is a cold-water fish with higher fat and omega-3 content than leaner fish.It contains 1.8 grams of creatine per pound, or nearly 0.45 grams per 4-ounce serving.
Bluefin tuna is one of the few food sources of vitamin D, with 5.7 micrograms per 3.5 ounces (100 grams), or 28% of the DV. The same serving contains 36.5 micrograms of selenium, or 66% of the DV. It is also a source of heart-healthy B vitamins.
U.S. Department of Agriculture: FoodData Central. Fish, tuna, fresh, bluefin, raw.
Bluefin tuna is commonly used in sushi and is sometimes available canned.

8. Pork
Creatine: 0.57 grams per 4-ounce serving
Pork contains 2.3 grams of creatine per pound raw, providing 0.57 grams per 4-ounce serving.Pork also provides high-quality protein, B-complex vitamins, and essential minerals like iron and zinc.
Pork loin, the leanest cut of pork, contains moderate levels of saturated fat compared to beef. It also has a balanced fatty acid profile, with nearly equal amounts of monounsaturated and saturated fatty acids.
How does creatine monohydrate work?
Creatine monohydrate rapidly replenishes ATP (adenosine triphosphate) by increasing phosphocreatine reserves in muscle cells, thus delaying muscle fatigue during high-intensity exercise. The specific mechanisms of action are as follows:
- Energy Replenishment Mechanism
Rapid ATP Synthesis: During high-intensity exercise, muscle contraction relies on ATP breakdown for energy. Creatine monohydrate combines with phosphate under the action of creatine kinase to generate phosphocreatine. When ATP is consumed as ADP, phosphocreatine can rapidly transfer phosphate groups to ADP, regenerating ATP and maintaining energy supply.
Maintaining Energy Metabolic Balance: Increasing phosphocreatine reserves stabilizes muscle energy supply and prevents fatigue caused by sudden energy drops.
- Metabolic Regulation Mechanism
Reducing Lactic Acid Accumulation: By improving intracellular buffering capacity, it delays the decrease in muscle pH, mitigating the impact of lactic acid accumulation on muscle function.
Optimizing Metabolic Product Transport: It promotes the excretion of metabolic products such as lactic acid, reducing the concentration of intracellular metabolic products.
- Cellular Level Effects
Enhancing Cellular Hydration: It increases intracellular water in muscle cells, maintains cell morphology and function, and improves the efficiency of nutrient transport.
Promotes protein synthesis: Increases muscle strength and endurance by increasing cell osmotic pressure and activating the mTOR signaling pathway.
6 reasons to take creatine monohydrate
1. Enhance-High-Intensity Performance
Creatine monohydrate enhances high-intensity exercise performance by increasing the storage of phosphocreatine in muscles, thereby helping to regenerate ATP (the body’s energy currency) during short bursts of intense exercise. This helps improve strength, power output, and the ability to perform more work in resistance training and high-intensity interval training. Creatine also aids in recovery, muscle growth, and enhances resistance to fatigue.
- ATP Regeneration: During intense exercise, ATP is rapidly broken down for energy. Creatine provides a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), rapidly regenerating ATP and enabling muscles to sustain high-intensity exercise.
- Increased Energy Supply: By increasing phosphocreatine storage, creatine supplementation ensures more available energy during high-intensity, short-duration exercise.
- Enhanced Training Adaptability: The ability to perform more work during training can lead to greater muscle mass, strength, and power gains over time.
Benefits of Creatine Monohydrate in Improving Athletic Performance
- Enhanced Strength and Power: Due to enhanced energy production, athletes can lift heavier weights or sprint faster.
- Improve sprint and interval training performance: Both single-repetition and repetitive sprint performance are enhanced.
- Enhance exercise endurance: You can complete more repetitions or sets during high-intensity training.
- Accelerate recovery: Creatine helps muscles recover faster during high-intensity training or rest between sets.

2. Promote Muscle Growth & Strength
Creatine monohydrate promotes muscle growth and strength by increasing the availability of energy for high-intensity exercise, allowing individuals to perform more work during training sessions, leading to greater adaptations in muscle mass and strength over time. Supplementation helps regenerate ATP, the body’s primary energy source, during short, explosive bursts of activity, which can improve performance in activities like weightlifting, sprinting, and jumping.
How creatine promotes muscle growth and strength?
- Increases energy for high-intensity bursts: Creatine supplements increase the body’s stores of phosphocreatine, which regenerates ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to provide quick energy for short, powerful movements.
- Allows for more training volume: By providing more energy, creatine can enable you to complete more repetitions or sets during a workout, leading to greater muscle stimulation and growth.
- Boosts muscle mass: Regular creatine supplementation, especially when combined with resistance training, has been shown to increase lean muscle mass and skeletal muscle mass.
- Enhances strength and power: Many studies show that creatine supplementation increases muscular strength and power output, especially in trained individuals.
Who benefits from creatine?
- Athletes in power and high-intensity sports: Creatine is particularly beneficial for athletes in sports that involve repeated high-intensity bursts and require rapid recovery, such as weightlifting, sprinting, and sports like soccer or hockey.
- Older adults: Some research suggests creatine can help older adults maintain muscle mass and bone density, potentially reducing the risk of falls.
- Individuals with sedentary lifestyles: Creatine can be effective for building muscle mass even for those who are not elite athletes, though the gains may be more modest.

3. Accelerate Recovery & Reduce Fatigue
Creatine monohydrate can accelerate recovery and reduce fatigue by mitigating exercise-induced muscle damage and aiding in the faster recovery of muscle function. It works by increasing the body’s ability to resynthesize ATP, the primary energy source for muscle contractions, and by exerting anti-inflammatory and membrane-stabilising effects that help reduce soreness and fatigue after intense exercise.
How it works
- Aids in muscle repair: Creatine supplementation has been shown to reduce exercise-induced muscle damage, leading to faster recovery after intense workouts.
- Enhances energy production: It increases the intracellular stores of phosphocreatine, which helps muscles resynthesize ATP more quickly, allowing them to work longer and harder.
- Reduces inflammation: Creatine may have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce the soreness and fatigue that follow intense exercise.
- Improves muscle function: Studies show it can accelerate the recovery of maximal voluntary muscle contraction (MVC) after strenuous activity.
- Lowers perceived exertion: Some research indicates creatine can reduce the perception of effort during workouts.
Benefits for athletes
- Faster recovery between sessions: The accelerated recovery may allow athletes to resume high-intensity training sooner, reducing downtime and maintaining performance levels.
- Improved performance: By reducing fatigue and improving recovery, it can help athletes handle their training load more effectively and reduce the risk of overtraining or injury.
- Useful in rehabilitation: Its ability to help muscles recover functional capacity may be beneficial in rehabilitation settings.
4. Support Brain & Cognitive Function
Creatine monohydrate may support brain and cognitive function by improving memory, attention, and processing speed, especially in older adults or during periods of metabolic stress like sleep deprivation. Studies have shown benefits across various cognitive tasks, though more research is needed to confirm these effects and determine optimal protocols for different populations. It is recommended to consult a healthcare provider before taking creatine supplements.
How it works
- Energy supply: Creatine is critical for supplying energy to the brain, which is a high-energy-demand organ.
- Increased brain creatine: Supplementation can increase the amount of creatine stored in the brain, with one study showing an 11% increase after a 6-week intervention.
- Neuroprotection: Creatine may offer neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which can protect nerve cells from damage.
Cognitive benefits
- Memory: Creatine supplementation has been linked to improvements in long-term memory.
- Attention and processing speed: Some studies report benefits in tasks measuring sustained attention and the speed at which information is processed.
- Executive function: Research suggests potential improvements in executive function, which includes skills like planning, focus, and problem-solving.
- Specific populations: Benefits may be more pronounced in older adults, vegetarians, or those with lower baseline creatine levels, and during stressful situations like sleep deprivation.

5. Promote Bone & Metabolic Health
Creatine monohydrate can promote bone and metabolic health, particularly when combined with resistance training. It may help improve bone density and strength, and decrease bone breakdown. Metabolically, it supports muscle energy production, can act as an antioxidant, and may help with age-related decline in muscle mass.
Studies indicate that creatine monohydrate may have auxiliary effects on bone density, glucose metabolism, and cardiovascular health, primarily by improving muscle mass, which indirectly benefits bone health, and potentially influencing glucose uptake and vascular function. These benefits are often observed in conjunction with exercise, such as resistance training, and may have potential applications for conditions like osteoporosis and heart failure.
- Muscle-bone link: Creatine supplementation, especially when combined with resistance training, can increase muscle mass and strength. This can stimulate bone formation, which may help increase bone mineral density and strength in older adults.
- Preserved bone mineral density (BMD): Studies found that women who engaged in resistance training and took creatine had a reduced rate of bone mineral loss at the femoral neck compared to those who only did resistance training. One 12-month study showed this combination could preserve femoral neck BMD in postmenopausal women.
- Increased bone bending strength: The combination of resistance training and creatine supplementation has been shown to increase femoral shaft width, which is a predictor of greater bone bending
6. Proven Safety & Affordability (Well-Studied Form)
Safety track record
- Several studies have reported that humans may safely consume creatine monohydrate.
- Researchers have stated that there is neither long-term nor short-term evidence that using creatine monohydrate has any negative consequences.
- Research has stated that using creatine monohydrate is safe for two to five years and even at larger dosages.
- Creatine increases the water content of muscle cells, hence increasing muscular mass.
Affordable
- Creatine monohydrate is the least expensive and simplest to get as a single component due to several factors.
- Creatine monohydrate may be less expensive to produce because it has been accessible for a longer period than other creatine forms.
- In addition, numerous varieties of this supplement are produced, which help keep pricing competitive.
- In most circumstances, the same size-types of creatine may be more expensive to purchase.
- Other versions of creatine as single components are difficult to find.
- As a result, monohydrate is the most affordable form of creatine available today.
The Button Line
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound in the body that helps produce muscle energy. It’s also found in foods like red meat and fish and is a main ingredient in many sports supplements.
Creatine monohydrate is a popular supplement that enhances high-intensity, short-duration exercise performance by increasing the body’s energy supply, leading to improved strength, power, and muscle mass. It is considered safe for most people in the short term and has been studied for potential benefits beyond athletics, including cognitive and clinical applications. The most studied and effective form is creatine monohydrate, available as a powder that should be mixed with liquid or food.
Creatine is generally considered safe in recommended dosages for most healthy adults. However, speak with a healthcare provider before adding new supplements to your routine.
